Ambient occlusion
Intermediate Artist
Note
As with other depth-aware post effects, enabling ambient occlusion nullifies MSAA (multisample anti-aliasing).
Ambient occlusion darkens areas where light is occluded by opaque objects, such as corners and crevices. You can use it to add subtle realism to scenes.
Properties
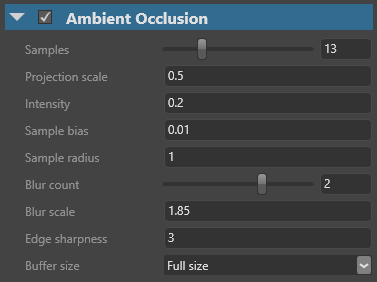
| Property | Function |
|---|---|
| Samples | The number of pixels sampled to determine how occluded a point is. Higher values reduce noise, but affect performance. Use with Blur count to find a balance between results and performance. |
| Projection scale | Scales the sample radius. In most cases, 1 (no scaling) produces the most accurate result. |
| Intensity | The strength of the darkening effect in occluded areas |
| Sample bias | The angle at which Stride considers an area of geometry an occluder. At high values, only narrow joins and crevices are considered occluders. |
| Sample radius | Use with projection scale to control the radius of the occlusion effect |
| Blur count | The number of times the ambient occlusion image is blurred. Higher numbers reduce noise, but can produce artifacts. |
| Blur scale | The blur radius in pixels |
| Edge sharpness | How much the blur respects the depth differences of occluded areas. Lower numbers create more blur, but might blur unwanted areas (ie beyond occluded areas). |
| Buffer size | The resolution the ambient occlusion is calculated at. The result is upscaled to the game resolution. Larger sizes produce better results but use more memory and affect performance. |